The Ultimate Guide to DPF Filters & DEF Systems on Semi Trucks
Let’s break down how to maintain peak emissions performance and avoid excessive repairs.
In this guide we’ll cover the various Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) and Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) products and their functions, from gaskets and clamps to slipcovers.
DPF and DEF systems aren’t related in any way. But they’re both critical aftertreatment systems for toxic exhaust emissions on a big rig.
Diesel Particulate Filters: The History, The Controversy

Before 2003, there weren't many regulations on Class 8 truck exhaust. Trucks had basic mufflers to help dampen noise, but nothing for exhaust fumes.
By 2003, all diesel engines were required to have Tier 2 emissions regulations. This included adding a catalyzing muffler to help reduce greenhouse emissions.
By 2008, more emissions regulations rolled out, namely the introduction of DPF (diesel particulate filter) systems.
By 2011, federal legislation mandated that all 2011 or newer diesels must have Selectrive Catalytics Reduction (SCR) Systems. SRC and DEF systems work closely together with DPF systems.
The downside?
They raise average exhaust temperatures by 30%, averaging between 750-1,100 F. This is why exhaust stacks need specialized chroming to prevent from flaking or discoloration.
Federal law mandates that DPF, DEF, and SCR system cannot be removed if they're factory installed.
Needless to say, these aftermarket treatment systems are a bit controversial; some drivers complain they decrease fuel economy and increase backflow – AND they aren’t cheap to replace. A new DPF or DEF filter can cost thousands of dollars.
What are they?
Let's start here.
What is a DEF (Diesel Exhaust Fluid) Filter?
Diesel exhaust fluid filters are a non-toxic EPA-mandated solution to HOz emissions on selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems.
DEF filters:
- Deisel exhaust fluid = 32.5% urea + 67.5% deionized water.
- Urea/water mixture is sprayed into hot exhaust, turns to ammonia, and kills toxic NOx levels
You should replace your DEF urea filter every 120,000 to 150,000 miles.
What Is a DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter)?

The DPF is basically a big metal tube that has porous screens within it; a DPF tends to trap and remove 85–100% of excess soot from the particulate matter (hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide) found in diesel exhaust.
If DPFs aren’t taken care of and soot is left to clog up the filter, the backpressure from the restricted exhaust flow will affect the engine.
How do you eliminate the soot? You burn it at really high temperatures. DPFs use regeneration techniques.
The regen system adds that extra energy to the exhaust to help burn off soot. During this process, ash accumulates.
As a result, you'll still need to replace or clean your DPF filter every 100,000 to 300,000 miles (or 4,500 hours). The frequency will depend on the engine's health and driving conditions.
DPF Regeneration: Burning Particulate
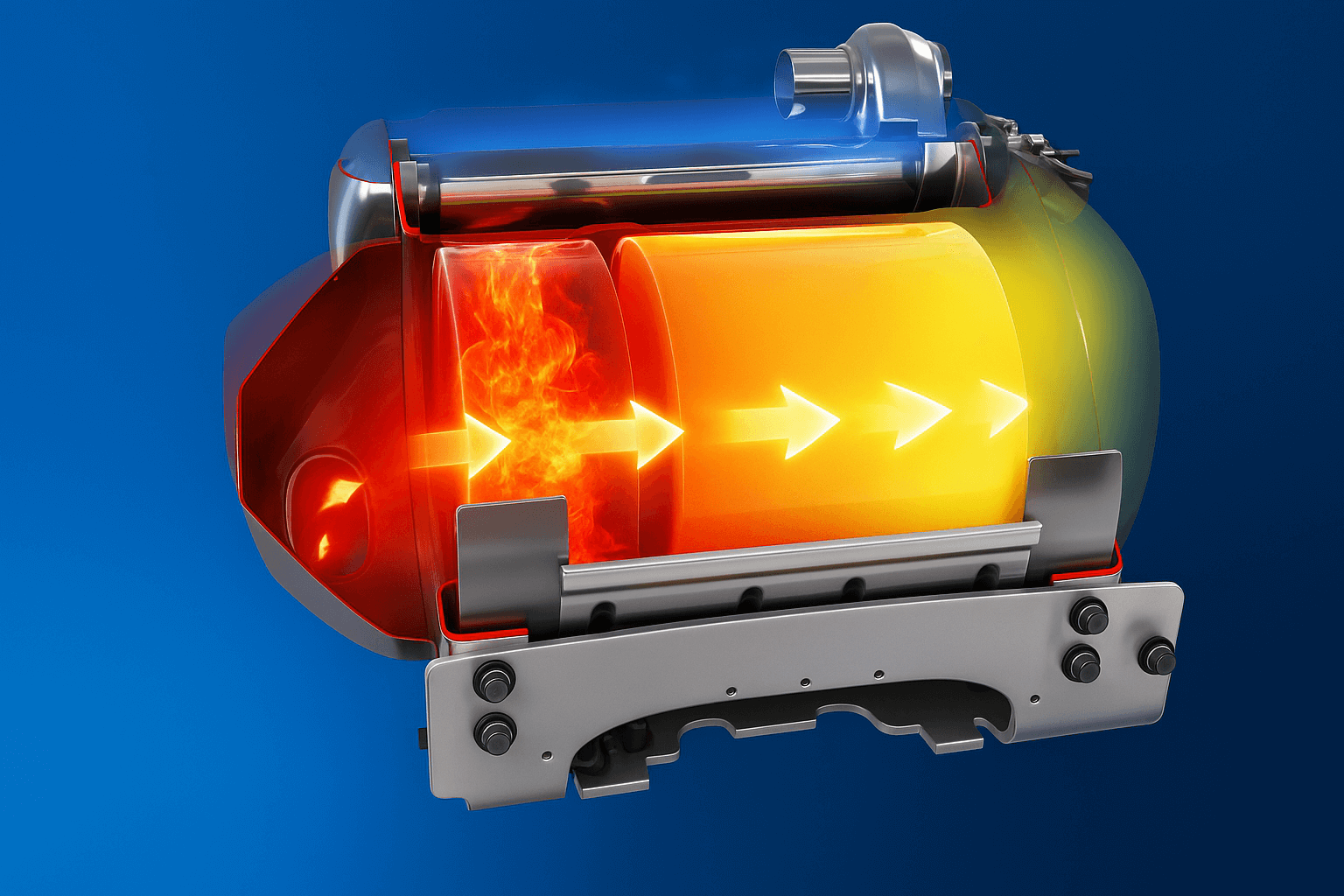
Regeneration is the process of burning off particulate matter (soot) into carbon dioxide during normal engine operation.
There are 3 types of regeneration:
- Passive: Happens during high-speed, long hauls.
- Active: Injects extra fuel to burn soot at lower temps.
- Forced: Done in a shop using a scan tool when the filter is too clogged.
Failed regeneration leads to excess soot, increased fuel consumption, and the truck would derate before this would happen.
Frequent short trips, low speeds, and stop-and-go situations can potentially lead to clogged DPFs.
Why DPF and DEF Systems are Critical for Diesel Vehicles
Diesel engines aren’t perfect. They don’t burn 100% of the fuel cleanly. Over time, leftover fuel particulates accumulate in your engine and cause problems.
This is where (DPF) filters come in handy.
Normally, a large percentage of your fuel is burnt when accelerating. If you have black smoke billowing from your stacks as you accelerate, it means you’re increasing the fuel consumption, but your air intake isn’t keeping up with the pace.
That black soot is essentially leftover pieces of fuel that didn’t get burned. A lack of oxygen isn’t the only reason for soot; it might be a fuel injector issue, excess carbon deposits in the combustion chamber, etc.
Here's the point.
Your semi-truck engine needs enough oxygen to burn fuel correctly.
Diesel engines will burn lean: there’s more oxygen in their combustion than there is fuel. This helps complete a healthy combustion cycle, leaving only water and carbon dioxide behind.
Should you get black soot coming out of your stacks, it means you lack enough oxygen to burn all of the fuel.
What about the opposite?
Too much oxygen and not enough fuel combined with high heat and pressure = nitrous oxide (NOx) a combination of one part nitrogen and two parts oxygen.
It's a toxic emission. The DEF (the water/urea mixture) sprays into your exhaust system and works as an aftertreatment for hazardous NOx levels.
EPA Regulations & Aftertreatment System Requirements
- Since 2007, EPA emissions rules have forced Class 8 diesel trucks to use aftertreatment systems like DPF and SCR.
- These systems significantly reduce soot (particulate matter) and harmful nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions
- All diesel trucks today must run DPF and DEF systems to remain street legal.
Aftertreatment System Components Explained (Takeaways)
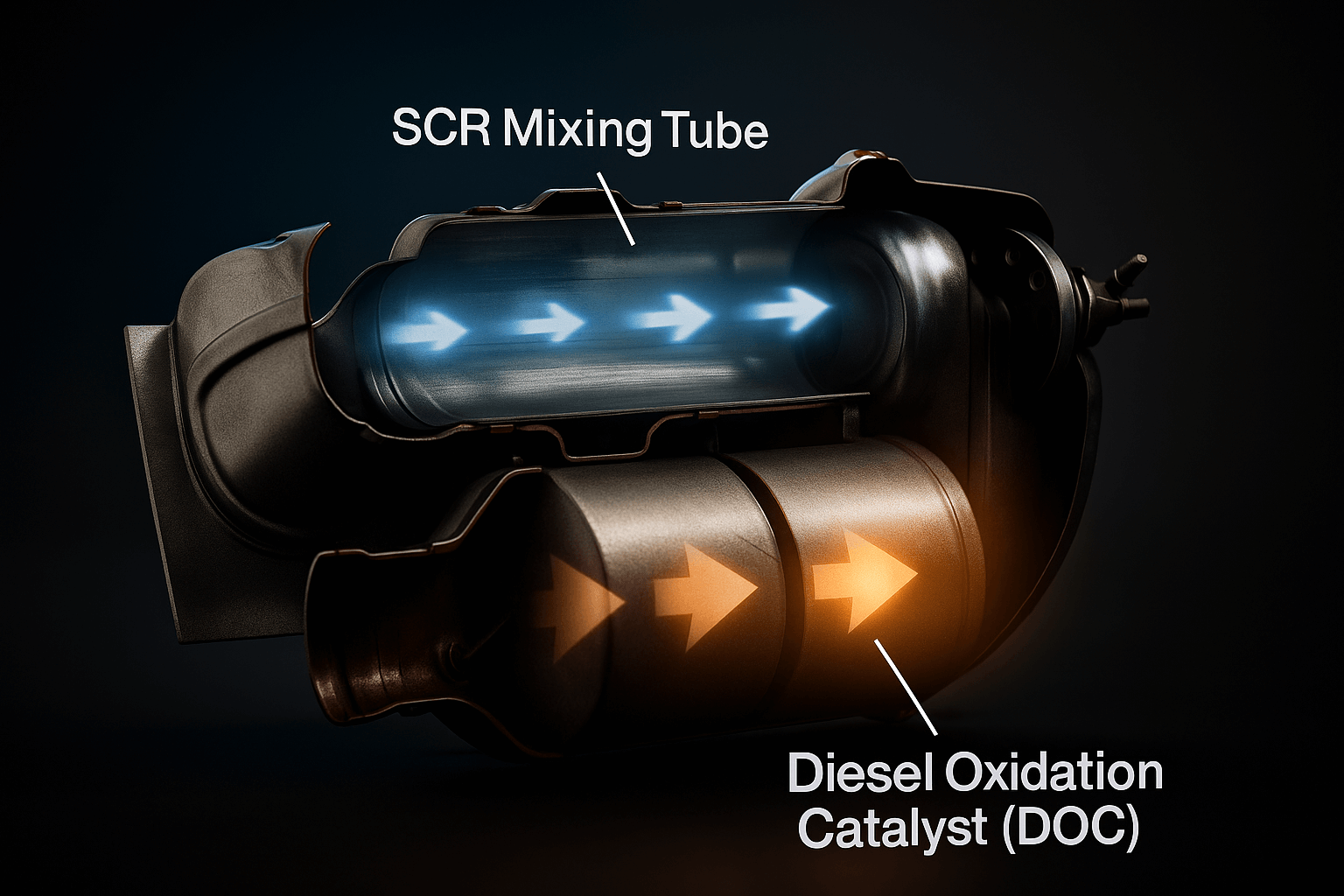
- DOC (Diesel Oxidation Catalyst): Preheats exhaust to start DPF regen.
- DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter): Traps soot and ash. Needs regular cleaning.
- SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction): Uses DEF to break down NOx into nitrogen and water vapor.
- DPF Maintenance is unavoidable and expensive. Clogging and ash buildup are common.
- DPF Differential Pressure Sensor (AKA soot sensor) monitors backpressure to trigger the regen process.
- Temperature sensors help control system behavior by monitoring the exhaust gas heat at various points to regulate the regen process.
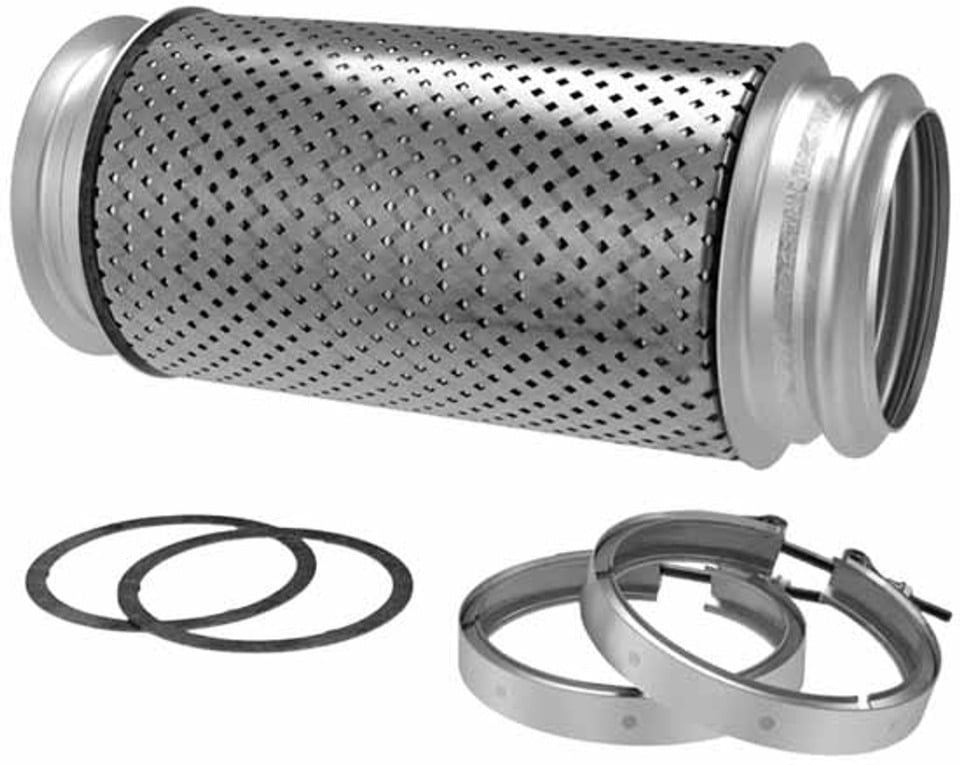

- Additional accessories for your DPF can include: gaskets, clamps, and chrome DPF box covers.
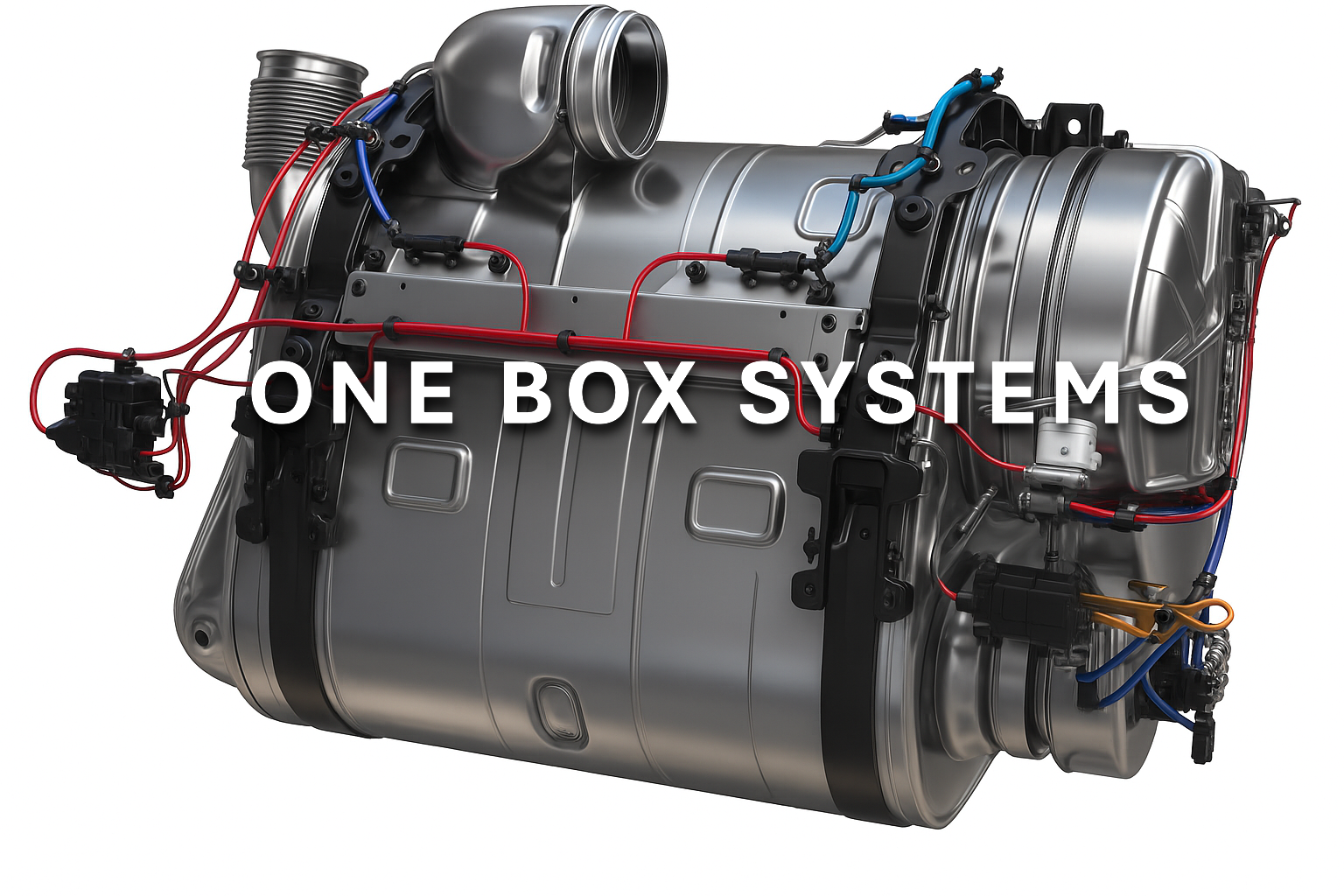
- DPF “One Box” system integrates DOC, DPF, and SCR into one system for simplified maintenance and a compact design that saves space around your frame rails.
A lot of new semi-truck model engines have this:
- Mack trucks’ ClearTech One System
- Trucks with a Detroit DD13, DD15, and DD16
- Volvo VNM, VNL, and VAH models with a D11 or D13 engine.
Components That Maintain Your Aftertreatment System
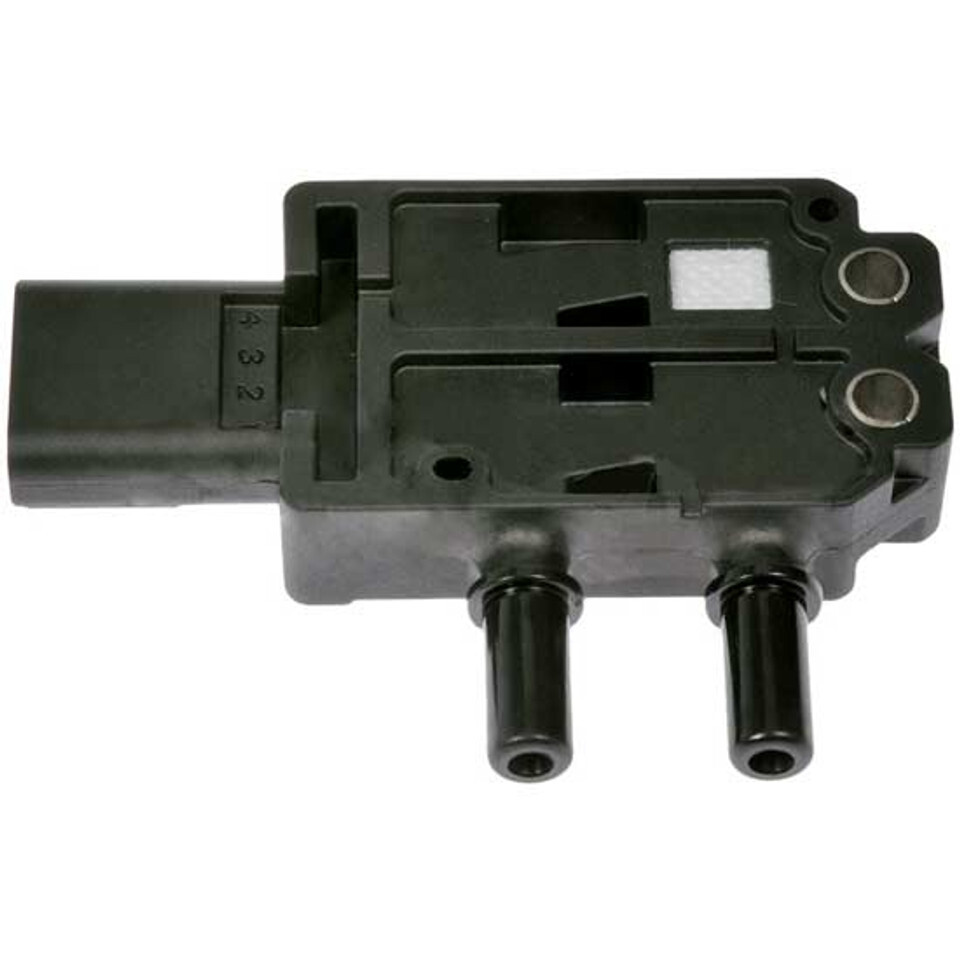
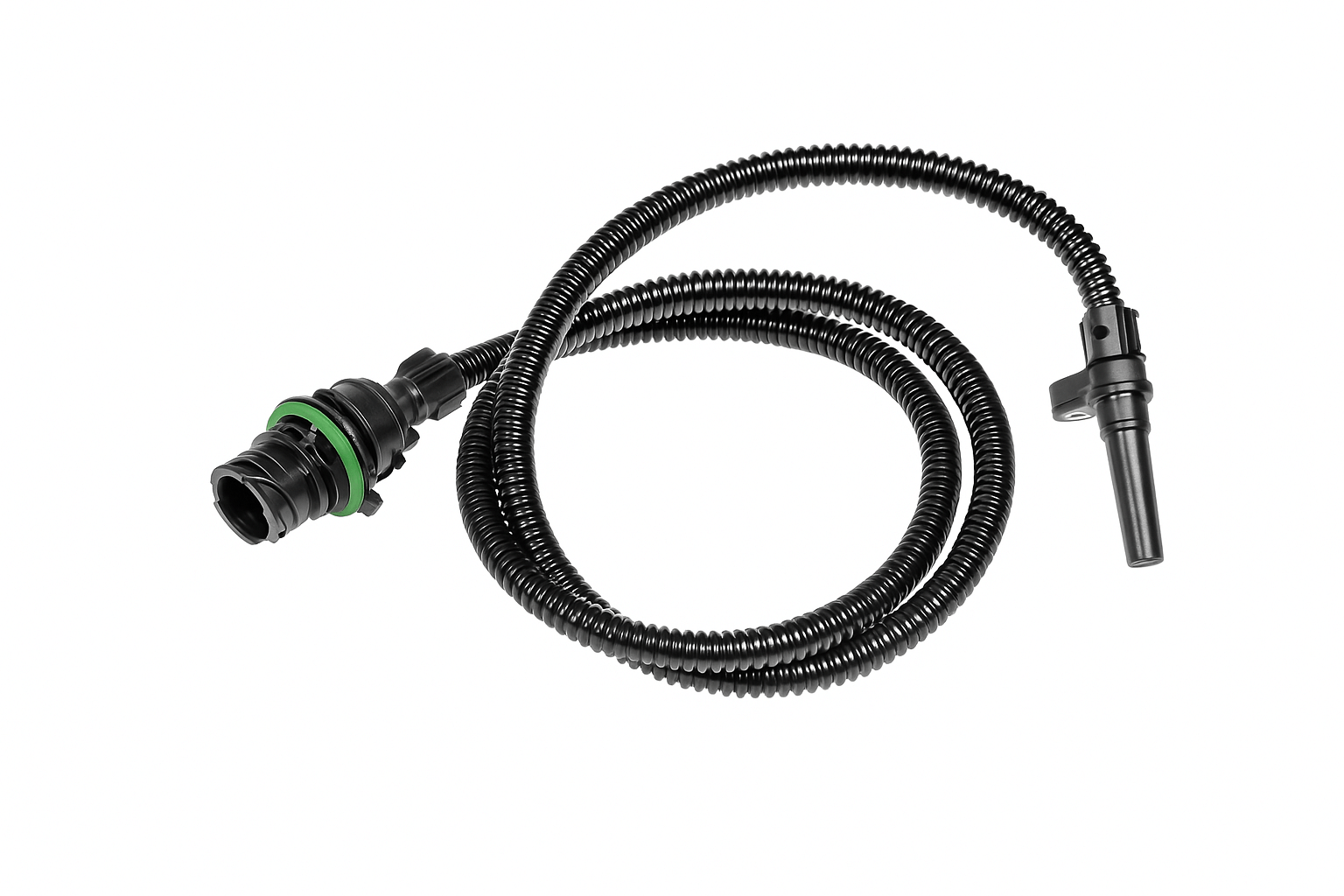
Differential Pressure Sensors

DPF differential pressure sensors are critical for measuring the exhaust backpressure.
The sensor has two silicon hoses that connect directly to the DPF: one is before the filter (higher up) and the other is after the filter (lower down).
It compares the exhaust pressure at both points. This is how the DPF sensor estimates how much soot buildup there is, whether there is a drop in exhaust pressure, or higher-than-normal pressure.
It takes this information and sends it to Engine Control Unit (ECU) – basically the “brain” of the semi-truck. The ECU determines if/when the regen cycle should trigger the ACM (Aftertreatment Control Module), burning off that excess soot.
Replacing your faulty sensor is way cheaper than getting a full DPF cleaning or replacement. When shopping for an aftermarket replacement, you’ll need a sensor compatible with your semi-truck engine type.
DPF Gaskets and Clamps

DPF Gaskets and DPF clamps ensure leak-free exhaust flow. Gaskets provide an airtight seal in your exhaust and aftertreatment system. They basically maintain the efficiency of your diesel engine by deterring any system leaks.
DPF clamps, usually V-clamps, clamp down different flanges of your aftertreatment components, stabilizing your system against road vibrations and the constant hot/cold cycles. Properly installing a DPF clamp is a critical task left to a professional technician.
DPF Covers

Get a polished, custom look while protecting your DPF unit from road debris. Most DPF covers come in standard 304 stainless steel finishes and can act as a replacement for your front panel DPF box or as a slipcover. A slipcover basically “slips onto” the existing DPF unit.
The Slipcover Depends on Your Semi Truck Model

Peterbilt 589: on a grass burner (exhaust comes out underneath) the same cover will fit both sides, driver and passenger side. If exhaust comes out of both sides, it’s a normal DPF. The battery box cover WILL NOT fit a DPF unit.
Product: Valley Chrome Plating SS DPF Filter Cover
Product: Peterbilt 389 Lower Box Cover
The Top Warning Signs of a Blocked DPF or Failing System
- Dashboard warning light indicators
- Poor acceleration, rough idle, increased fuel use, and frequent regen cycles
- Diagnosing early signs of DPF failure to avoid total filter replacement
- Risk of engine derate or complete shutdown from ignoring a blocked DPF
Common DPF Problems & Solutions
Problem Signs:
- Clogging from excessive soot and ash.
- Regen failures from low temps, bad sensors, or driver habits.
- Cracking or melting from runaway regen caused by hydrocarbon slip.
Solutions:
- Frequent highway drives (for passive regen).
- Scheduled DPF cleaning every 100k–200k miles.
- Address upstream issues (bad injectors, EGR, coolant/oil leaks).
- Don’t ignore dash lights—train drivers to react early.
Common DEF System Failures
DEF Crystallization:
- Freezes at 12°F or breaks down above 86°F.
- Crystals clog filters, lines, and injectors.
DEF Contamination:
- DEF is easily spoiled by diesel, oil, dirt, or tap water.
- Causes injector failure, poor NOx control, engine derates.
DEF Pump & Injector Failures:
- Can result from contaminated/crystallized DEF or wear.
Sensor Failures:
- Bad NOx or DEF level sensors send wrong data to the ECM.
Freezing Issues:
- DEF lines and tanks must be heated in cold climates to prevent freezing.
Storage Issues:
- DEF goes bad if exposed to heat, sunlight, or air.
- Use only dedicated containers and sealed systems.
DEF Troubleshooting Tips
- Use a refractometer to check DEF urea concentration (should be 32.5%).
- Cloudy, smelly, or colored DEF = contaminated.
- Don’t mix DEF with other fluids (cross-contaminated).
- Replace contaminated or expired DEF immediately.
Preventative Maintenance Tips
- Inspect DPF/DEF systems regularly (ideally when refueling).
- Clean DPFs every 100k–200k miles.
- Monitor regen frequency and address if increasing.
- Never skip engine diagnostics—DPF/DEF problems often start with engine faults.
- Train drivers to allow regen cycles and report warning lights early.
- Regular system flushes to remove buildup or minor crystallization
- DEF tank heater inspections while in cold climates
Model-Specific Notes (Peterbilt, Kenworth, Freightliner, etc.)
- Common problems apply to all, but sensor placement and part compatibility vary.
- Peterbilt and Kenworth: Pressure sensors and DEF contamination are fairly frequent issues.
- Freightliner: DEF injector failures and “One Box” system troubles can occur.
- International: DPF clogs and DEF system errors.
- Volvo: DEF crystallization and sensor issues often lead to derates.
Final DPF/DEF Takeaways for Fleet Managers & Owner-Operators
- DPFs require both regeneration and physical cleaning due to ash accumulation.
- DEF must be pure, fresh, and handled properly to avoid costly repairs down the line.
- Sensors are vital—if they fail, the whole system can suffer.
- Proactive maintenance and driver training are your best defense.
- Always use ISO-certified DEF and CJ-4/CK-4 low-ash oils.
Now that you know a bit more about these critical filters, consider buying your next replacement DPF filter or DEF filter online at 4 State Trucks or by using our mobile app!
Recent Posts
-
13 Must-Have Kenworth Chrome Accessories (For Any Budget)
If you're looking for the perfect aftermarket chrome upgrades to give your Kenworth a polished, slee …13th Feb 2026 -
Why is GBATS the Most Unique Truck Show in America?
GBATS (Guilty By Association Truck Show) is a massive 3-day event that has the atmosphere of a carni …6th Feb 2026 -
Peterbilt vs Freightliner: Which Semi Truck Is the Right Truck for Owner Operators?
Looking to buy your next highway truck? If you’re choosing between Freightliner and Peterbilt to be …30th Jan 2026 -
7 Best Trux Accessories LED Lighting Upgrades to Customize Your Rig
In the world of aftermarket truck parts brands, the competition is fierce. With hundreds of manufact …23rd Jan 2026 -
Fiberglass Fenders vs Aluminum & Poly Fenders: Which Material Wins?
A stylish semi truck fender is among the best way to personalize and cusotmize your big rig. But whe …16th Jan 2026 -
Haul of Fame: The Rat Rod (Custom-Built Peterbilt 359)
Bryan Martin. A Peterbilt 359. Over a decade of scars, stories, and soul. Some trucks come and go …16th Jan 2026 -
How Fibertech's Fiberglass Truck Parts Improve Airflow & Aesthetics
Fibertech truck parts, known for their Fibertech fenders, whale tales, and sleeper roof caps, delive …9th Jan 2026 -
Peterbilt vs Mack: Choosing Between Rugged or Classic Styles
Let’s do a quick breakdown of Mack trucks vs Peterbilt trucks. Mack is naturally the cheaper, more a …2nd Jan 2026 -
How to Choose the Best Refrigerator for Your Semi Truck
Every OTR truck driver needs reliable cooling for food and beverages on long haul drives. That's whe …26th Dec 2025